CenterNet : Keypoint Triplets for Object Detection
Abstract
- In object detection, keypoint-based approaches often suffer a large number of incorrect object bounding boxes, arguably due to the lack of an additional look into the cropped regions.
-
객체 검출에 있어서, 키포인트기반의 접근법들은 많은 수의 일치하지 않는 객체 바운딩 박스를 제공하는데 이는 잘린 지역들에서의 추가적인 정보의 부족 때문이다.
- This paper presents an efficient solution which explores the visual patterns within each cropped region with minimal costs.
-
이 논문은 최소한의 비용으로 각 잘려진 지역안에서의 시각적 패턴의 탐색하는 효율적인 해결책을 제시한다.
- Our approach, named CenterNet, detects each object as a triplet, rather than a pair,of keypoints, which improves both precision and recall.
-
우리의 접근법인 CenterNet은 객체의 키포인트의 한 쌍이 아닌 세 쌍을 검출함으로써 precision과 recall 둘 다 향상시킨다.
- We designed two customized modules named “cascade corner pooling” and “center pooling”, which play the roles of enriching information collected by both top-left and bottom-right corners and providing more recognizable information at the central regions, respectively.
- 두가지 모듈인 “cascade corner pooling” 과 “center pooling” 을 만들었고, 이는 상단-좌측과 하단-우측 코너로부터 일치하는 정보를 풍부화하는 역할을하며, 중심지역에서 각각 더 인식 가능한 정보를 제공한다.
Introduction
- In the current era, one of the most popular flowcharts is anchor-based, which placed a set of rectangles with pre-defined sizes, and regressed them to the desired place with the help of ground-truth objects.
-
현재 시대에 가장 널리 사용되는 flowchars중 하나는 앵커 기반이며, 이는 사전에 정의된 크기의 사각형 세트를 배치하고 실측 객체의 도움으로 원하는 위치로 회귀합니다.
- These approaches often need a large number of anchors to ensure a sufficiently high IoU(intersection over union) rate with the ground-truth objects, and the size and aspect ratio of each anchor box need to be manually designed.
-
이러한 접근법들은 실측 객체와의 충분히 높은 IoU(교집합 / 합집합)보장하기 위하여 많은 수의 앵커들이 필요하고, 각 앵커박스의 크기와 종횡비는 수동적으로 설계되어져야합니다.
- In addition, anchors are usually not aligned with the ground-truth boxes, which is not conducive to the bounding box classification task..
-
또한 앵커는 일반적으로 실측상자와 정렬되지 않기 때문에 바운딩 박스 분류 업무에 도움이 되지 않습니다.
- To overcome the drawbacks of anchor-based approahces, a keypoint-based object detection pipline named CornerNet was proposed.
-
앵커 기반 접근 방식의 단점을 극복하기 위해 키포인트 기반의 객체 검출 파이프 라인인 CornerNet이 제안되었다.
- It represented each object by a parir of corner keypoints, which bypassed the need of anchor boxes and achieved the state-of-the-art one-stage object detection accuracy.
-
이는 각 객체의 코너 키포인트의 쌍을 표현함으로써 가장 성능이 좋은 one-stage 객체 검출 정확도를 성취하면서 앵커 박스들의 필요성을 제거했습니다.
- Nevertheless, the performance of CornerNet is still restricted by its relatively weak ability of referring to the global information of an object.
-
그렇지만, CornerNet의 성능은 객체의 전역 정보를 참조하는 상대적으로 약한 기능으로 인해서 제한됩니다.
- That is to say, since each object is constructed by a pair of corners, the algorithm is sensitive to detect the boundary of objects, meanwhile not being aware of which pair of keypoints should be grouped into obects.
- 이말은 즉, 각 객체는 한 쌍의 모퉁이들로 구성됨으로써 이 알고리즘은 객체의 경계를 검출하는데 민감하며, 그동안에 어떠한 키포인트의 쌍이 객체로 그룹화되어야 하는지를 모릅니다.
- Consequently, as shown in Figure 1, it often generates some incorrect bounding boxes, most of which could be easily filtered out with complementary information, e.g., the aspect ratio.
-
결과적으로 그림 1과 같이 일부 잘못된 경계 상자가 생성되는 경우가 많으며, 대부분 가로 세로 비율과 같은 보완 정보로 쉽게 필터링 할 수 있습니다.
- The address this issue, we equip CornerNet with an ability of perceiving the visual patterns within each proposed region, so that it can identify the correctness of each bounding box by itself.
-
이 문제를 해결하기 위해 CornerNet은 각 제안 된 영역 내에서 시각적 패턴을 인식하는 기능을 갖추게하기 때문에 각 경계 상자의 정확성을 자체적으로 식별 할 수 있습니다.
- In this paper, we present a low-cost yet effective solution named CenterNet, which explores the central part of a proposal, i.e., the region that is close to the geometric center, with one extra keypoint.
-
이 논문에서는, CenterNet 이라는 저렴한 비용의 효과적인 솔루션을 제시합니다. 이 솔루션은 제안의 중심 부분, 즉 기하학적 중심에 가까운 지역을 하나의 키포인트로 탐색합니다.
- Our intuition is that, if a predicted bounding box has a high IoU with the ground-truth box, then the probability that the center keypoint in its central region is predicted as the same class is hihgh, and vice versa.
-
우리의 직감은 예측 된 경계 상자가지면 진실 상자와 높은 IoU를 갖는 경우 중앙 영역의 중심 키포인트가 같은 클래스가 높을수록 예측 될 수 있으며 그 반대도 마찬가지입니다.
- Thus, during inference, after a proposal is generated as a pair of corner keypoints, we determine if the proposal is indeed an object by checking if there is a center keypoint of the same class falling within its central region. The idea, as shown in Figure 1, is to use a triplet, instead of a pair, of keypoints to represent each object.
-
따라서 추론 중에 제안이 한 쌍의 모퉁이 키포인트로 생성 된 후 동일한 지역의 중심 키포인트가 중심 영역 내에 있는지 확인하여 제안이 실제로 객체인지 여부를 결정합니다. 그림 1과 같이 아이디어는 쌍 대신 키포인트의 세 쌍을 사용하여 각 객체를 나타냅니다.
- Accordingly, for better detecting center keypoints and corners, we propose two strategies to enrich center and corner information, respectively.
-
따라서 중심점과 모서리를보다 잘 감지하기 위해 중심점과 모서리 정보를 보강하는 두 가지 전략을 제안합니다.
- cener pooling : It is used in the branch for predicting center keypoints. Center pooling helps the center keypoints obtain more recognizable visual patterns within objects, which makes it easier to perceive the central part of a proposal.
- 중심점 예측을 위해 지점에서 사용됩니다. 센터 풀링을 사용하면 센터 키포인트가 개체 내에서 더 잘 보이는 시각적 패턴을 얻을 수 있으므로 제안서의 중심 부분을보다 쉽게 인식 할 수 있습니다.
- We achieve this by getting out the max summed response in both horizontal and vertical directions of the center keypoint on a feature map for predicting center keypoints.
-
중심 키포인트를 예측하기위한 기능 맵에서 중심 키포인트의 수평 및 수직 방향으로 최대 합산 응답을 가져와 이를 달성합니다.
- cascade corner pooling which equips the original corner pooling module with the ability of perceiving internal information.
-
이것은 원래의 corner pooling 모듈에 내부 정보를 인식하는 능력을 갖추고 있습니다. - We achieve this by getting out the max summed response in both boundary and internal directions of objects on a feature map for predicting corners. - 모서리를 예측하기 위해 특징 맵에서 객체의 경계와 내부 방향 모두에서 최대 합산 응답을 가져 와서 이를 달성합니다.
- Empirically, we verify that such a two-directional pooling method is more stable, i.e., being more robust to feature-level noises, which contributes to the improvement of both precision and recall.
- 경험적으로, 우리는 이러한 양방향 풀링 방법이 더 안정적이며, 즉 특징-레벨 노이즈에 대해 보다 견고하기에 정확성과 리콜의 개선에 기여하는지 검증합니다.
Related Work
- Object detection involves locating and classifying the objects. In the deep learning era, powered by deep convolutional neural networks, object detection approaches can be roughly categorized into two main types of piplines, namely, two-stage approaches and one-stage approaches.
- 물체 감지에는 물체를 찾아 분류하는 것이 포함됩니다. 딥 컨벌루션 신경망에 의해 구동되는 딥 러닝 시대에, 객체 검출 접근법은 크게 2 가지 주요 유형, 즉 two-stage 접근법 및 one-stage 접근법으로 분류 될 수있다.
- Two-stage approaches divide the object detection task into two stages: extract RoIs, then classify and regress the RoIs.
-
Two-stage 접근법 은 RoI추출과 RoI(Region of Interest)들의 분류와 회귀인 2 단계로 객체 검출 업무를 나눈다.
-
R-CNN & Fast-RCNN & Faster-RCNN & Mask-RCNN등 많은 논문에서 언급했기에 해당 설명 부분은 생략
- The keypoint-based object detection approaches are proposed to avoid the disadvantages of using anchor boxes and bounding boxes regression.
-
키포인트 기반의 검출 방식은 바운딩 박스들을 회귀와 앵커박스들을 사용함으로 인해 생기는 불이익을 회피하기 위해 제안되었다.
- Other meaningful works are proposed for different problems in object detection, e.g., focus on the architecture design, focus on the contextual relationship, focus on the multi-scale unification.
-
다른 의미있는 작업은 객체 탐지의 다른 문제, 예를 들어 아키텍처 디자인에 초점을 맞추고 상황에 관계를 두고 멀티 스케일 합침에 초점을두고 제안됩니다.
- One-stage approaches remove the RoI extraction process and directly classify and regress the candidate anchor boxes.
-
One-stage 접근법 은 RoI추출 과정을 제거하고 직접적으로 후보 앵커 박스들을 회귀하고 분류합니다.
-
Two-stage approaches와 마찬가지로 상세 설명 부분은 생략함
-
CornerNet is another keypoint-based approach, which directly detect an object using a pair of corners. Alothough CornetNet achieve high performance, it still has more room to improve.
- CornerNet 은 또다른 키포인트 기반의 접근법이며 이는 직접적으로 코너의 한 쌍을 사용하여 객체를 검출한다. 비록 CornerNet이 높은 성능을 얻을지라도 그것은 여전히 개선할 점이 많다.
Our approach
Baseline and Motivation
- This paper uses CornerNet as the basline. For detecting corners, CornerNet produces, two heatmaps: a heatmap of top-left corners and a heatmap of bottom-right corners.
-
이 논문은 CornerNet을 기본베이스로 사용한다. 모퉁이들을 검출하기 위해서, CornerNet는 두개의 히트맵을 생성합니다 : 상단-좌축 모퉁이와 하단-우측 모퉁이의 히트맵
- The heatmaps represent the locations of keypoints of different categories and assignes a confidence score for each keypoint. Besides, it also predicts an embedding and a group of offsets for each corner.
-
이 히트맵들은 다른 분류들의 키포인트의 위치를 나타내며 각 키포인트에 대한 신뢰도 점수를 할당합니다. 또한, 각 모서리에 대한 오프셋들의 그룹과 임베딩을 예측합니다.
- The embeddings are used to identify if two corners are from the same object. The offsets learn to remap the corners from the heatmaps to the input image.
-
임베딩은 두개의 모퉁이가 같은 객체인지를 확인하기 위해 사용됩니다. 오프셋들은 히트맵에서 입력 이미지로부터 모서리를 다시 연결하기 위해 학습합니다.
- For generating object bounding boxes, top-k left-top corners and bottom-right corners are selected from the heatmaps according to their scores, respectively.
-
객체 바운딩 박스들을 생성하기위해, 최상위-k 좌측 상단 코너와 하단-우측 코너들은 반복적으로 점수에 따라 히트맵으로부터 선택됩니다.
- Then, the distance of the embedding vectors of a pair of corners is calculated to determine if the paired corners belong to the same object.
-
그 다음, 한 쌍의 코너의 임베딩 벡터의 거리는 한 쌍의 코너가 동일한 객체에 속하는지 여부를 결정하기 위하여 계산된다.
- An object bounding box is generated if the distance is less than a threshold. The bounding box is assigned a confidence score, which equals to the average scores of the corner pair.
- 거리가 임계 값보다 작은 경우 객체 경계 상자가 생성됩니다. 경계 상자에는 모서리 쌍의 평균 점수와 동일한 신뢰 점수가 할당됩니다.
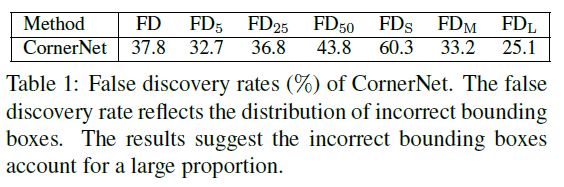
- FD : False discovery rates (잘못된 발견 비율)
- The quantitative reresults demonstrate the incorrect bounding boxes account for a large proportion even at low IoU thresholds, e.g., CornerNet obtains 32.7% FD rate at IoU = 0.05.
-
정량적 결과는 IoU 임계 값이 낮더라도 잘못된 경계 상자가 큰 비율을 차지함을 보여줍니다. 예를 들어 CornerNet은 IoU = 0.05에서 32.7 % FD 비율를 얻습니다.
- This means in average, 32.7 out of every 100 object bounding boxes have IoU lower than 0.05 with the ground-truth. The small incorrect bounding boxes are even more, which achieves 60.3% FD rate.
-
이는 평균적으로 100 개의 객체 경계 상자 중 32.7 개가 IoU가 0.05보다 낮으며 기본적으로 참임을 의미합니다. 작고 잘못된 경계 상자는 훨씬 더 많아서 FD 비율이 60.3 %에 이릅니다.
- One of the possible reasons lies in that CornerNet cannot look into the regions inside the bounding boxes.
-
가능한 이유 중 하나는 CornerNet이 경계 상자 내부의 영역을 볼 수 없기 때문입니다.
- To make CornerNet perceive the visual patterns in bounding boxes, one potential solution is to adapt CornerNet into a two-stage detector, which uses the RoI pooling to look into the visual patterns in bounding boxes. However, it is known that such a paradigm is computationally expensive.
-
CornerNet이 경계 상자에서 시각적 패턴을 인식하게하려면 CornerNet을 two-stage 감지기에 적응시키는 것이며 이는 RoI 풀링을 사용하여 경계 상자의 시각적 패턴을 조사하는 것입니다. 그러나 이러한 패러다임은 계산 비용이 많이 드는 것으로 알려져 있습니다.
- In this paper, we propose a highly efficient alternative called CenterNet to explore the visual patterns within each bounding box.
-
본 논문에서는 각 경계 상자 내의 시각적 패턴을 탐색하기위한 CenterNet이라는 매우 효율적인 대안을 제안합니다.
- For detecting an object, our approach uses a triplet, rather than a pair, of keypoints. By doing so, our approach is still a one-stage detector, but partially inherits the functionality of RoI pooling.
-
우리의 접근 방식은 물체를 감지하기 위해 한 쌍의 키포인트가 아닌 세 쌍을 사용합니다. 그렇게함으로써 우리의 접근 방식은 여전히 one-stage 탐지기이지만 RoI 풀링의 기능을 부분적으로 상속합니다.
- Our apporach only pays attention to the center information, the cost of our approach is minimal. Meanwhile, we further introudce the visual patterns within objects into the keypoint detection process by using center pooling and cascade corner pooling.
- 우리의 접근 방식은 센터 정보에만주의를 기울이고 접근 비용은 최소화됩니다. 한편 센터 풀링과 캐스케이드 코너 풀링을 사용하여 객체 내의 시각적 패턴을 키포인트 감지 프로세스에 추가로 소개합니다.
Object Detection as Keypoint Triplets
- The overall network architecture is shown in Figure 2. We represent each object by a center keypoint and a pair of corners. Specifically, we embed a heatmap for the center keypoints on the basis of CornerNet and predict the offsets of the center keypoints. Then, we use the method proposed in CornerNet to generate top-k bounding boxes.
-
전체 네트워크 아키텍처는 그림 2에 나와 있습니다. 각 키포인트와 중심 키포인트로 각 객체를 나타냅니다. 특히 CornerNet을 기준으로 중심 키포인트에 대한 히트 맵을 포함시키고 중심 키포인트의 오프셋을 예측합니다. 그런 다음 CornerNet에서 제안한 방법을 사용하여 top-k 경계 상자를 생성합니다.
- However, to effectively filter out the incorrect bounding boxes, we leverage the detected center keypoints and resort to the following procedure:
-
그러나 잘못된 경계 상자를 효과적으로 필터링하기 위해 감지 된 중심 키포인트를 활용하고 다음 절차를 따릅니다.
- select top-k center keypoints according to their scores
- 점수에 따라 top -k 센터 키포인트를 선택하십시오
- use the corresponding offsets to remap these center keypoints to the input image
- 입력 이미지에 중심 키포인트를 재매핑하기 위해서 일치하는 오프셋을 사용
- define a central region for each bounding box and check if the central region contains center keypoints. Note that the class labels of the checked center keypoints should be same as that of the bounding box
- 각 경계 상자의 중앙 영역을 정의하고 중앙 영역에 중앙 키포인트가 있는지 확인하십시오. 체크 된 중심 키포인트의 클래스 레이블은 경계 상자의 클래스 레이블과 동일해야합니다.
- if a center keypoint is detected in the central region, we will preserve the boudning box. The score of the bounding box will be replaced by the average scores of the three points, i.e., the top-left corner, the bottom-right corner and the center keypoint. If there are no center keypoints detected in its central region, the bounding box will be removeed.
- 중앙 영역에서 중심 키포인트가 감지되면, 바운딩 박스를 보존합니다. 바운딩 박스의 점수는 세 개의 점의 평균 점수, 즉 좌측 상단 코너, 우측 하단 코너 및 중앙 키포인트로 대체 될 것이다. 중앙 영역에서 중심 키포인트가 감지되지 않으면 경계 상자가 제거됩니다.
- select top-k center keypoints according to their scores
- The size of the central region in the bounding box affects the detection results. For example, smaller central regions lead to a low recall rate for small bounding boxes, while larger central regions lead to a low precision for large bounding boxes.
-
경계 상자의 중앙 영역 크기는 감지 결과에 영향을줍니다. 예를 들어 중앙 영역이 작을수록 작은 경계 상자의 리콜 비율 낮아지고 중앙 영역이 클수록 큰 경계 상자의 정밀도가 떨어집니다.
- Therefore, we propose a scale-aware central region to adaptively fit the size of bounding boxes. The scale-aware central region tends to generate a relatively large central region for a small bounding box.
- 따라서 우리는 경계 상자의 크기에 맞게 스케일을 인식하는 중앙 영역을 제안합니다. 스케일 인식 중앙 영역은 작은 경계 상자에 대해 비교적 큰 중앙 영역을 생성하는 경향이 있습니다.
- In this paper, n is set to be 3 and 5 for the scales of bounding boxes less and greater than 150, respectively. Figure3 shows two central regions when n = 3 and n = 5, a scale-aware central region, then we check if the central region contains center keypoints.
- 이 논문에서, 경계 상자의 스케일이 각각 150보다 작거나 큰 경우 n은 3과 5로 설정됩니다. 그림 3은 스케일 인식 중앙 영역 인 n = 3 및 n = 5 인 경우 두 개의 중앙 영역을 표시 한 다음 중앙 영역에 중심 키포인트가 있는지 확인합니다.
Enriching Center and Corner Information
- Center pooling
- The geometric centers of objects do not necessarily convey very recognizable visual patters (e.g., the human head contains strong visual patterns, but the center keypoint is often in the middle of the human body.)
-
물체의 기하학적 중심은 인식 할 수있는 시각적 패턴을 반드시 전달할 필요는 없습니다 (예 : 사람의 머리에는 강한 시각적 패턴이 포함되어 있지만 중심 키포인트는 종종 인체의 중간에 있습니다).
- To address this issue, we propose center pooling to capture richer and more recognizable visual patters.
-
이 문제를 해결하기 위해보다 풍부하고 인식 가능한 시각적 패턴을 캡처 할 수 있는 센터 풀링을 제안합니다.
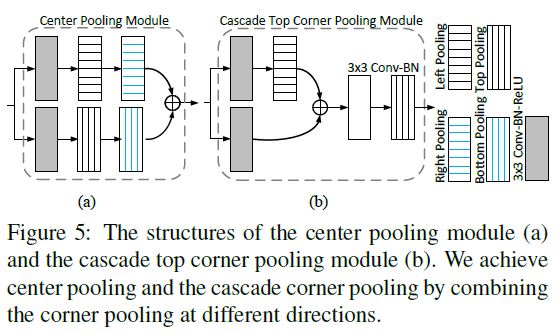
- Figure 4(a) shows the principle of center pooling.
- 그림 4 (a)는 센터 풀링의 원리를 보여줍니다.
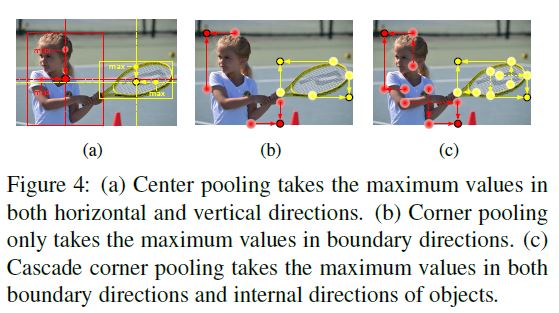
- The backbone outputs a feature map, and to determine if a pixel in the feature map is a center keypoint, we need to find the maximum value in its both horizontal and vertical directions and add them together. By doing this, center pooling helps the better detection of center keypoints.
-
백본은 피쳐 맵을 출력하고 피쳐 맵의 픽셀이 중심 키포인트인지 확인하려면 가로 및 세로 방향에서 최대 값을 찾아 함께 추가해야합니다. 이를 통해 센터 풀링은 센터 키포인트를 더 잘 감지하는 데 도움이됩니다.
- Cascade corner pooling
- Corners are often outside the objects, which lacks local appearance features. CornerNet uses corner pooling to address this issue. The principle of corner pooling is shown in Figure 4(b).
-
모서리는 종종 개체 외부에 있으며 로컬 모양 기능이 없습니다. CornerNet은이 문제를 해결하기 위해 코너 풀링을 사용합니다. 코너 풀링의 원리는 그림 4 (b)에 나와 있습니다.
- Corner pooling aims to find the maximum values on the boundary directions so as to determine corners. However, it makes corners sensitive to the edges.
-
코너 풀링은 코너를 결정하기 위해 경계 방향에서 최대 값을 찾는 것을 목표로합니다. 그러나 그것은 모서리를 가장자리에 민감하게 만듭니다.
- To adress this problem, we need to let corners “see” the visual patterns of objects. The priciple of cascade corner pooling is presented in Figure 4(c).
-
이 문제를 해결하려면 모서리가 객체의 시각적 패턴을 “보도록”해야합니다. 계단식 코너 풀링의 원리는 그림 4 (c)에 나와 있습니다.
- It first looks along a boundary to find a boundary maximum value, then looks inside along the location of the boundary maximum value to find an internal maximum value, and finally, add the two maximum values together.
-
먼저 경계를 따라 경계 최대 값을 찾은 다음 경계 최대 값의 위치를 따라 내부 최대 값을 찾은 다음 마지막으로 두 최대 값을 더합니다.
- By doing this, the corners obtain both the boundary information and the visual patterns of objects.
- 이를 통해 모서리는 경계 정보와 객체의 시각적 패턴을 모두 얻습니다.
- Both the center pooling and the cascade corner pooling can be easily achieved by combining the corner pooling at different directions.
- 중앙 풀링과 계단식 코너 풀링은 코너 풀링을 서로 다른 방향으로 결합하여 쉽게 달성 할 수 있습니다.
- Figure 5(a) shows the structure of the center pooling module. To take a maximum value in a direction, e.g., the horizontal direction, we only need to connect the left pooling and the right pooling in series.
-
그림 5 (a)는 중앙 풀링 모듈의 구조를 보여줍니다. 가로 방향과 같은 방향으로 최대 값을 얻으려면 왼쪽 풀링과 오른쪽 풀링을 직렬로 연결하기 만하면됩니다.
- Figure 5(b) shows the structure of a cascade top corner pooling module.
-
그림 5 (b)는 캐스케이드 상단 코너 풀링 모듈의 구조를 보여줍니다.
- Compare with the top corner pooling in CornerNet, we add a left corner pooling before the top corner pooling.
- CornerNet의 상단 코너 풀링과 비교하여 상단 코너 풀링 전에 왼쪽 코너 풀링을 추가합니다.
Training and inference
- Training The resolution of the input image is 511 X 511, leading to heatmaps of size 128 X 128. We use the data augmentation strategy presented in [20] to train a robust model. Adam is used to optimize the training loss
-
입력 이미지의 해상도는 511 X 511이며, 크기는 128 X 128의 히트 맵으로 이어집니다. [20]에 제시된 데이터 확대 전략을 사용하여 강력한 모델을 학습시킵니다. Adam은 훈련 손실을 최적화하는 데 사용됩니다
- Inference
- hyper-parameter에 대한 정보이기 때문에 생략
Experiments
Dataset, Metrics and Baseline
-
We evaluate our method on the MS-COCO dataset. It contains 80 categories and more than 1.5 million object instances.
- AP : average precision rate is computed over ten different IoU(i.e., 0.5 : 0.05 : 0.95) and all categories.
- AP : 정밀도 비율의 평균 / 이는 10개의 다른 IoU범주(예시)와 모든 카테고리들(80개의 classes)에 대해서
- AR : maximum recall rate is computed over a fixed number of detections(i.e., 1,10 and 100) per image and averaged over all categories and the ten different IoU thresholds.
-
AR : 최대 리콜 비율 / 이는 고정된 검출 수에 대한 이미지당 계산되고 모든 카테고리에서의 평균와 다른 IoU 임계값들에 대해서
-
small object : 32^2보다 작은 객체
-
medium object : 32^2 < area < 96^2 중간 크기의 객체
- large object : 96^2보다 큰 객체
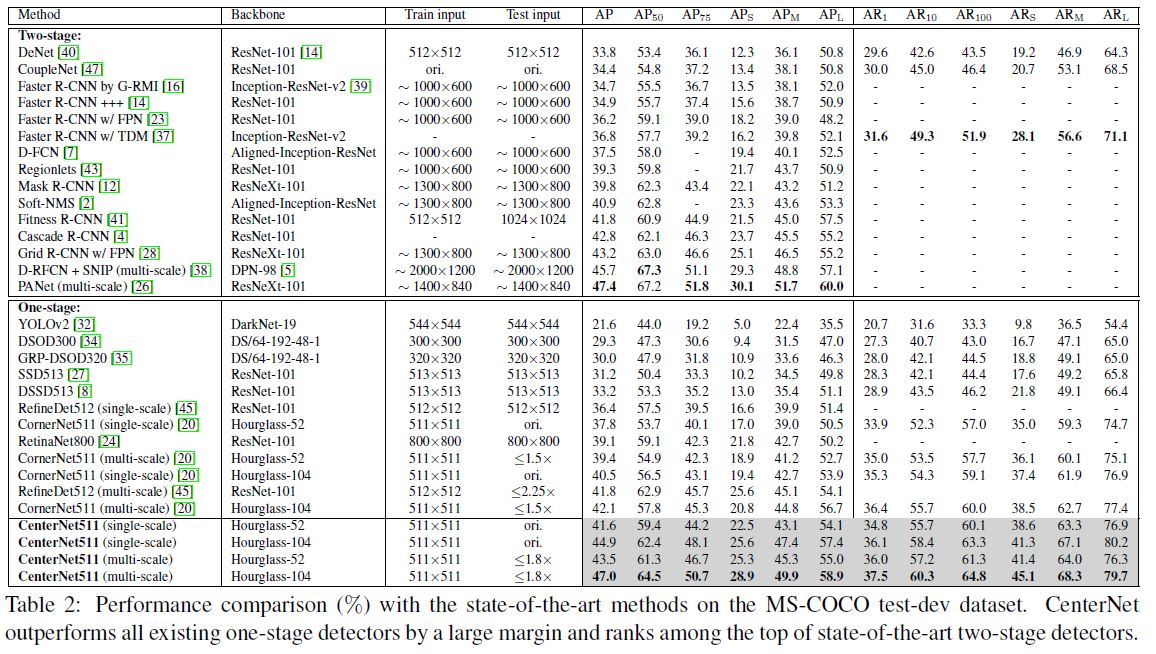
Comparison with State-of-the-art Detectors
- These results firmly demonstrate the effectiveness of CenterNet.
-
이러한 결과는 CenterNet의 효과를 확실하게 보여줍니다.
- Meanwhile, it can be seen that the most contribution comes from the small objects.
-
한편, 가장 큰 기여는 작은 물체에서 나온다는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
- The benefit stems from the center information modeled by the center keypoints: the smaller the scale of an incorrect bounding box is, the lower probability a center keypoint can be detected in its central region.
- 이점은 중심 키포인트에 의해 모델링 된 중심 정보에서 비롯됩니다. 잘못된 경계 상자의 스케일이 작을수록 중앙 키포인트가 중앙 영역에서 감지 될 가능성이 낮아집니다.
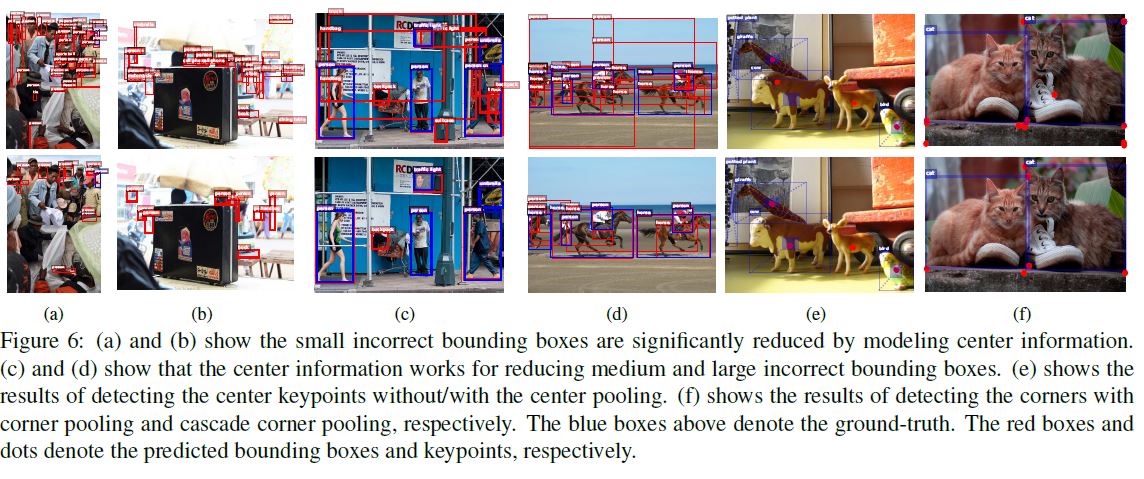
- Figure 6(a) and Figure 6(b) show some qualitative comparisons, which demonstrate the effectiveness of CenterNet in reducing small incorrect bounding boxes.
-
그림 6 (a)와 그림 6 (b)는 일부 부정확 한 경계 상자를 줄이는 데 CenterNet의 효과를 보여주는 질적인 비교를 보여줍니다.
- CenterNet also leads to a large improvement for reducing medium and large incorrect bounding boxes.
- CenterNet은 또한 중간 및 큰 잘못된 경계 상자를 줄이기 위해 크게 개선되었습니다.
- Figure 6(c) and Figure 6(d)) show some qualitative comparisons for reducing medium and large incorrect bounding boxes.
- 그림 6 (c)와 그림 6 (d)는 중간 및 큰 부정확 한 경계 상자를 줄이기위한 질적 비교를 보여줍니다.
- It is wort noting that the AR is also significantly improved, with the best performance achieved with multi-scale testing.
- 멀티 스케일 테스트를 통해 최고의 성능을 발휘하여 AR도 크게 개선되었다는 점에 주목할 필요가 있습니다.
- This is becaues our approach removes lots of incorrect bounding boxes, which is equivalent to improving the confidence of those bounding boxes with accurate locations but lower scores.
- 이것은 우리의 접근 방식이 잘못된 경계 상자를 많이 제거하기 때문에 정확한 위치이지만 점수가 낮은 경계 상자의 신뢰도를 향상시키는 것과 같습니다.
—
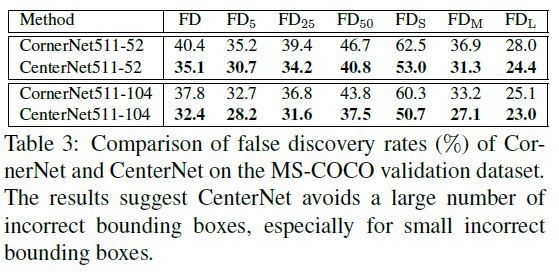
Incorrect Bounding Box Reduction
- Table 3 shows the FD rates for CornerNet and CenterNet. CornerNet generates many incorrect bounding boxes even at IoU = 0.05 threshold.
-
표 3은 CornerNet 및 CenterNet의 FD 비율을 보여줍니다. CornerNet은 IoU = 0.05 임계 값에서도 많은 잘못된 경계 상자를 생성합니다.
- On the other hand, CornerNet generates more small incorrect bounding boxes than medium and large incorrect bounding boxes.
-
반면에 CornerNet 잘못된 작은 경계상자들을 잘못된 중간과 큰 경계상자들보다 많이 생성합니다.
- Our CenterNet decreases the FD rates at all criteria via exploring central regions.
- CenterNet은 중앙 지역 탐색을 통해 모든 기준에서 FD 비율을 낮 춥니 다.
Inference Speed
- 생략
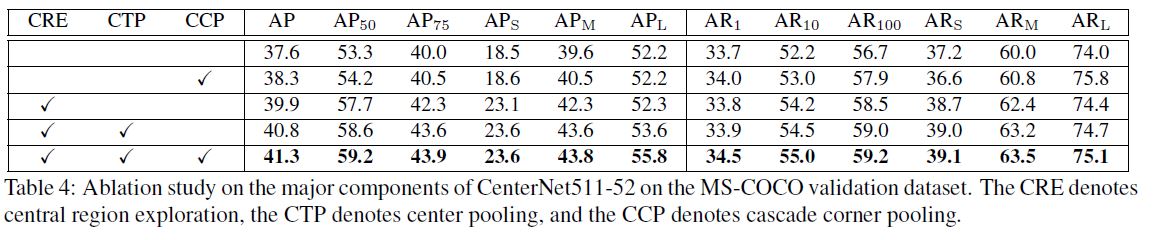
Ablation Study
- Our work has contributed three components, including central region exploration, center pooling and cascade corner pooling.
-
우리의 작업은 중앙 지역 탐사, 센터 풀링 및 계단식 코너 풀링을 포함하여 세 가지 구성 요소에 기여했습니다.
- To analyze the contribution of each individual component, an ablation study is given here.
-
각 개별 구성 요소의 기여도를 분석하기 위해 절제 연구가 제공됩니다.
- Central region exploration To understand the importance of the central region exploration, we add a center heatmap branch to the baseline and use a triplet of keypoints to detect bounding boxes.
-
중앙 영역 탐색의 중요성을 이해하기 위해 기준선에 중앙 히트 맵 분기를 추가하고 삼중점 키포인트를 사용하여 경계 상자를 감지합니다.
- For the center keypoint detection, we only use conventional convolutions.
- 중심 키포인트 감지의 경우 기존 컨볼 루션 만 사용합니다.
- We find that the improvement for the small objects (that is 4.6%) is more significant than that for other object scales.
-
작은 객체 (4.6 %)의 개선이 다른 객체 스케일의 개선보다 더 컸다는 것을 알았습니다.
- The improvement for large objects is almost negligible (from 52.2% to 52.3%).
-
큰 물체의 개선은 거의 무시할 만합니다 (52.2 %에서 52.3 %).
- This is not surprising because, from a probabilistic point of view, the center keypoint for a small object is easier to be located than that of a large object.
-
확률적인 관점에서 작은 물체의 중심 키포인트가 큰 물체의 중심 키포인트보다 위치하기 쉽기 때문에 이는 놀라운 일이 아닙니다.
- Center pooling To demonstrate the effectiveness of proposed center pooling, we then add the center pooling module to the network.
-
제안 된 센터 풀링의 효과를 보여주기 위해 센터 풀링 모듈을 네트워크에 추가합니다.
- It demonstrates that our center pooling is effective in detecting center keypoints of objects, especially for large objects.
-
중심 풀링은 특히 큰 오브젝트의 경우 오브젝트의 중심 키포인트를 감지하는 데 효과적이라는 것을 보여줍니다.
- Our explanation is that center pooling can extract richer internal visual patterns, and large objects contain more accessible internal visual patterns.
-
우리는 센터 풀링이 더 풍부한 내부 시각적 패턴을 추출 할 수 있으며 큰 객체에는 더 접근하기 쉬운 내부 시각적 패턴이 포함되어 있다고 설명합니다.
- Cascade corner pooling We replace corner pooling with cascade corner pooling to detect corners.
-
코너 풀링을 캐스케이드 코너 풀링으로 교체하여 코너를 감지합니다.
- The results of the second row show there is almost no change in the AP for large object ( i.e., 52.2% vs. 52.2%), but the AR is improved by 1.8% (from 74.0% to 75.8%).
-
두 번째 행의 결과는 큰 물체에 대한 AP의 변화가 거의 없음 (즉, 52.2 % 대 52.2 %)을 나타내지 만 AR은 1.8 % (74.0 %에서 75.8 %)로 개선되었습니다.
- This suggest that cascade corner pooling can “see” more objects, but too rich visual patterns may interfere with its perception for the boundary information, leading to many inaccurate bounding boxes.
-
이는 계단식 코너 풀링이 더 많은 객체를 “볼”수 있지만 너무 풍부한 시각적 패턴은 경계 정보에 대한 인식을 방해하여 많은 부정확 한 경계 상자로 이어질 수 있음을 나타냅니다.
- After equipping with our CenterNet, the inaccurate bounding boxes are effectively suppressed, which improves the AP for large object by 2.2% (from 53.6% to 55.8%).
- CenterNet을 장착 한 후 부정확 한 경계 상자가 효과적으로 억제되어 대형 물체의 AP가 2.2 % (53.6 %에서 55.8 %)로 향상되었습니다.
Error Analysis
- The exploration of visual patterns within each bounding box depends on the center keypoints. In other words, once a center keypoints is missed, the proposed CenterNet would miss the visual patterns within the bounding box.
-
각 경계 상자 내의 시각적 패턴 탐색은 중심 키포인트에 따라 다릅니다. 다시 말해, 중심 키포인트를 놓치면 제안 된 CenterNet은 경계 상자 내의 시각적 패턴을 놓치게됩니다.
- To understand the importance of center keypoints, we replace the predicted center keypoints with the ground-truth values and evaluate performance on the MS-COCO validation dataset.
-
중심 키포인트의 중요성을 이해하기 위해 예측 된 중심 키포인트를 실제 값으로 바꾸고 MS-COCO 유효성 검사 데이터 집합의 성능을 평가합니다.
- The result demonstrates that the detection of center keypoints is far from the bottlenect.
- 결과는 중심 키포인트 감지가 병목에서 멀리 떨어져 있음을 보여줍니다.
Conclusions
- CenterNet addresses the problem that CornerNet lacks an additional look into the cropped regions by exploring the visual patterns within each proposed region with minimal costs.
-
CenterNet은 최소한의 비용으로 제안 된 각 영역의 시각적 패턴을 탐색하여 CornerNet이 잘린 영역에 대한 추가보기가 부족한 문제를 해결합니다.
- As one-stage approaches remove the RoI extraction process, they cannot pay attention to internal information within cropped regions.
-
1 단계 접근 방식이 RoI 추출 프로세스를 제거하므로 자른 영역 내의 내부 정보에주의를 기울일 수 없습니다.
-
An intuitive explanation of our contribution lies in that we equip a one-stage detector with the ability of two-stage approaches, with an effcient discriminator being added.
- 우리의 기여도에 대한 직관적 인 설명은 1 단계 검출기에 2 단계 접근법의 능력을 갖추고 있으며 효율적인 판별 기가 추가된다는 것입니다.